beta one receptors|Beta 1 Receptors: Function, Significance, and Clinical : iloilo The beta-1 adrenergic receptor (β 1 adrenoceptor), also known as ADRB1, can refer to either the protein-encoding gene (gene ADRB1) or one of the four adrenergic receptors. [5] It is a G-protein coupled receptor associated with the Gs heterotrimeric G-protein that is expressed predominantly in cardiac tissue. How to work out an each-way bet. Here is an example of how to work out an each-way bet. You want to place an each-way bet on Love Envoi in the 2023 Champion Hurdle at the Cheltenham Festival. Her odds are 33/1 and there are 14 runners in the race which is not a handicap, which means that 1st, 2nd and 3rd places will be paid out at one fifth of .
beta one receptors,
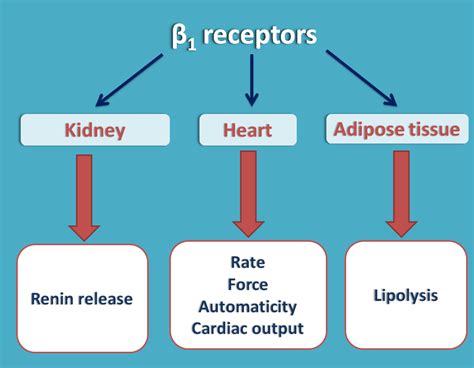
The beta 1 receptor is vital for the normal physiological function of the sympathetic nervous system. Through various cellular signaling mechanisms, hormones and medications activate the beta-1 receptor. Targeted activation of the beta-1 receptor increases heart rate, renin release, and lipolysis.

The beta-1 adrenergic receptor (β 1 adrenoceptor), also known as ADRB1, can refer to either the protein-encoding gene (gene ADRB1) or one of the four adrenergic receptors. [5] It is a G-protein coupled receptor associated with the Gs heterotrimeric G-protein that is expressed predominantly in cardiac tissue. Beta receptors are adrenergic receptors that respond to the neurotransmitters epinephrine (adrenaline) and norepinephrine (noradrenaline). They are part of the G-protein-coupled receptor family and play a crucial role in the sympathetic nervous system, responsible for the “fight or flight” response. Beta-1 receptors, along with beta-2, alpha-1, and alpha-2 receptors, are adrenergic receptors primarily responsible for signaling in the sympathetic nervous system. Beta-agonists bind to the beta receptors on various tissues throughout the body. Beta adrenergic receptors are one of two main adrenergic receptors, the other being alpha receptors. They are involved in generating a sympathetic response when activated by catecholamines such as norepinephrine or epinephrine.

The beta-1 adrenergic receptor, the dominant receptor in heart and adipose tissue, is equally sensitive to epinephrine and norepinephrine, whereas the beta-2 adrenergic receptor, responsible for relaxation of vascular, uterine, and airway smooth muscle, is less sensitive to norepinephrine than to epinephrine. The beta-3 receptor is insensitive .beta one receptorsThe beta-1 adrenergic receptor, the dominant receptor in heart and adipose tissue, is equally sensitive to epinephrine and norepinephrine, whereas the beta-2 adrenergic receptor, responsible for relaxation of vascular, uterine, and airway smooth muscle, is less sensitive to norepinephrine than to epinephrine. The beta-3 receptor is insensitive . Beta 1 receptors are a type of adrenergic receptor found in the heart, kidneys, and adipose tissue. They play a role in regulating heart rate and blood pressure. Learn more about beta 1 receptors, their functions, and associated conditions in this article.
Beta 1 Receptors: Function, Significance, and Clinical Beta-1 receptors are a type of adrenergic receptor found primarily in the heart. They belong to the G protein-coupled receptor family and are crucial for various physiological processes. Understanding what these receptors do is essential for grasping how our body responds to stress, regulates heart function, and manages blood pressure.
beta one receptors|Beta 1 Receptors: Function, Significance, and Clinical
PH0 · What Do Beta‑1 Receptors Do?
PH1 · Dissecting Beta
PH2 · Beta Receptors: A Complete Overview
PH3 · Beta 1 Receptors: Function, Significance, and Clinical
PH4 · Beta 1 Receptors
PH5 · Beta
PH6 · Adrenergic Receptors: Team Beta